I. Intro
Date: 02/08/2023
During the first lab, we went through how to query out the data we want.
II. Querying Data
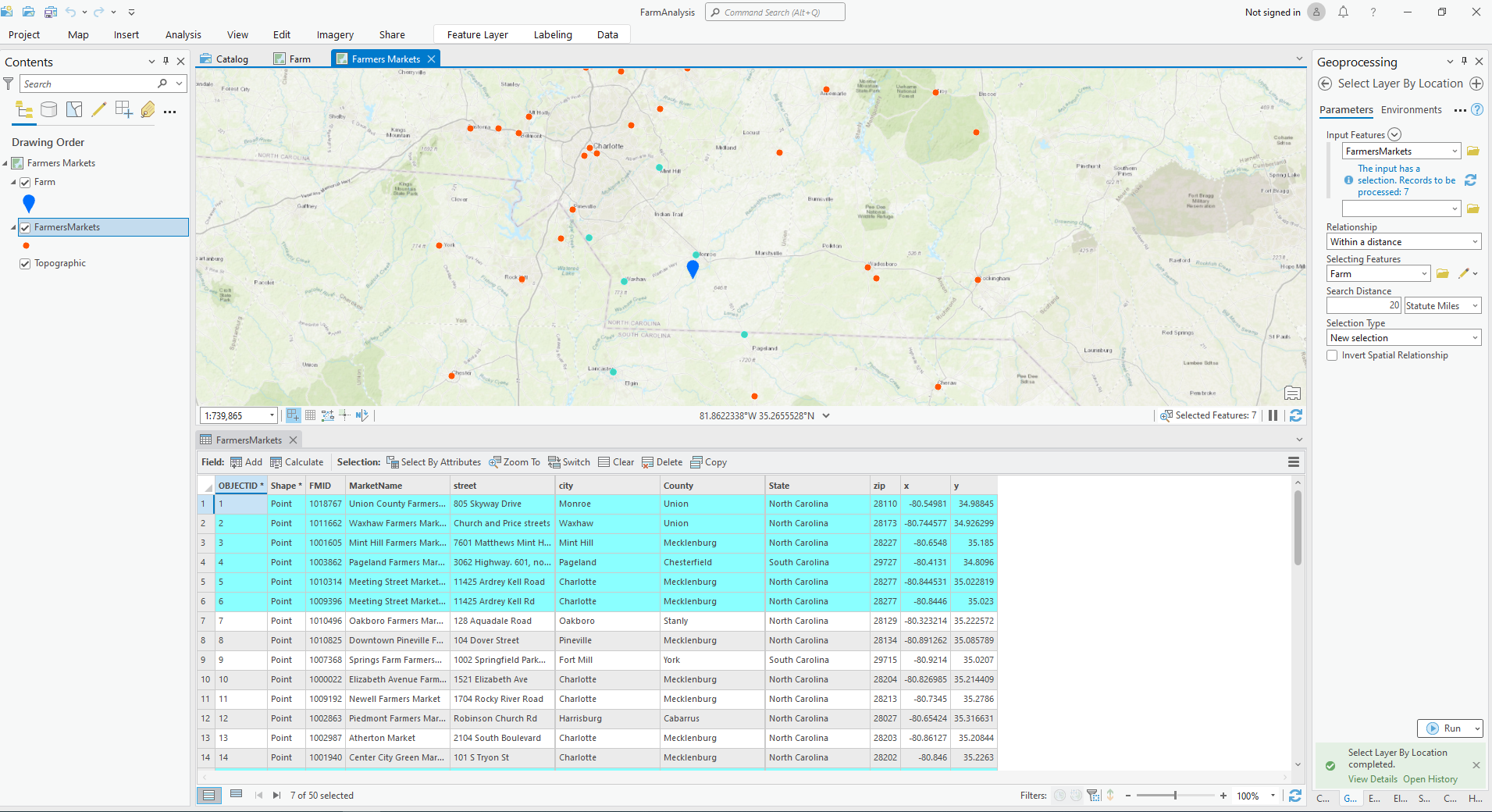
A. Attribute Field, Attribute Value, and Operator
- The field is the category of each set of data, value is the actual information with in the field. The operator helps us to find the values we want.
- Select the value for “heights of males are larger than 6 feet.”
- Height of male: the attribute field determines which field to query in the attribute table.
- 6 feet: the attribute value identifies the value that you are searching for in each record of the attribute table.
- Larger than: the operator represents the measurement that you will use to query a selection of features.
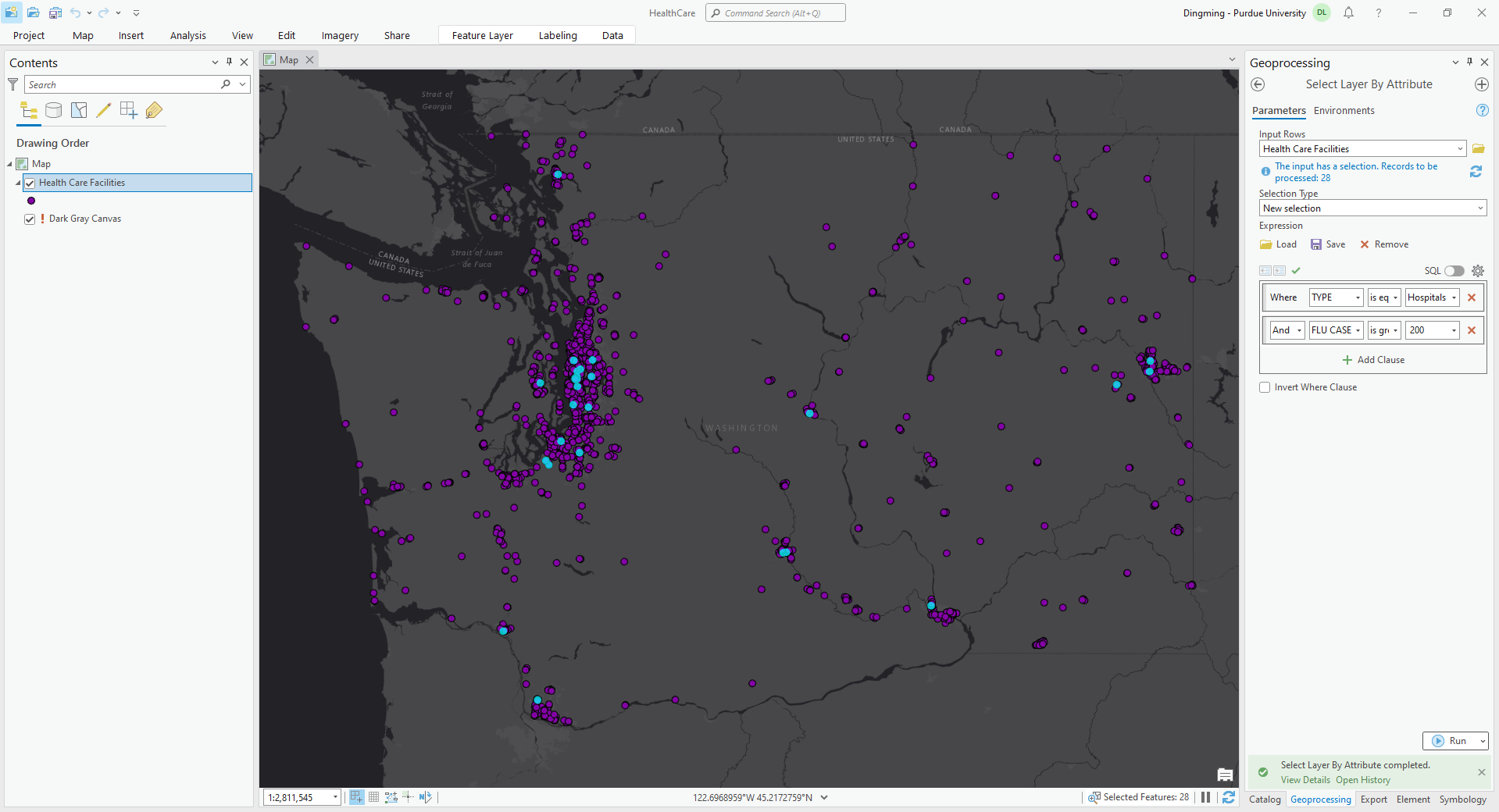
III. Spatial Relationships
- Touch: Any part of a feature from the first feature class must contact the boundary of a feature from the second feature class.
- Contain: A feature from the first feature class completely encloses a feature from the second feature class.
- Intersect: Features from the first feature class that come into contact with any part of a feature from the second feature class.
- Within: Similar to the contains spatial relationship, the within spatial relationship is when a feature from the second feature class completely encloses a feature from the first feature class.
- Cross: A feature from the first feature class comes into contact with the interior or boundary of a feature from the second feature class.
- Overlaps: The interior of a feature from the first feature class partly or completely covers a feature from the second feature class.
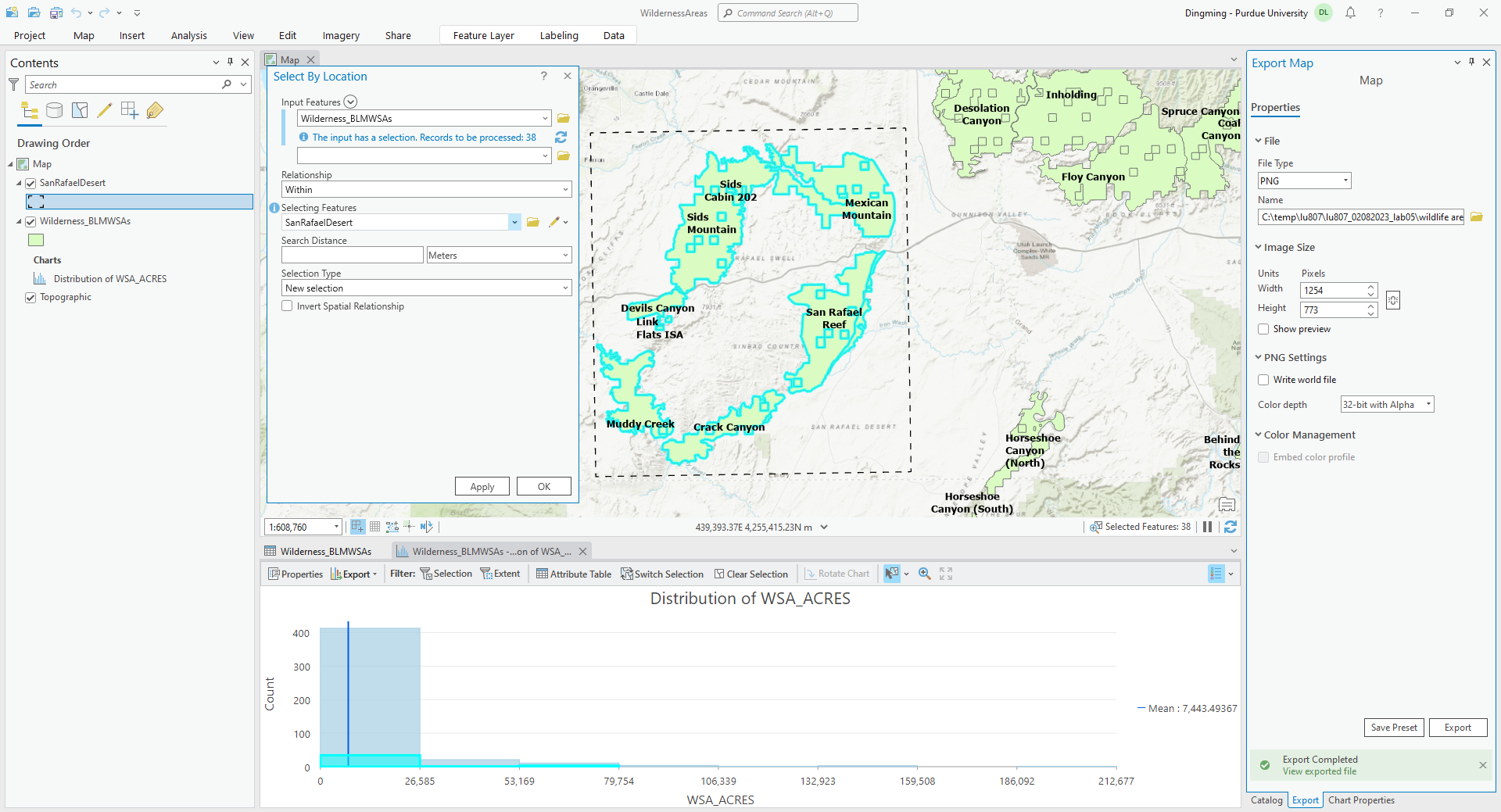
IV. Spatial Analysis
A. Six spatial analysis categories
- Understand where.
- Measure size, shape, distribution
- Determine how places are related
- Find the best locations and paths
- Detect and quantify patterns
- Make predictions
B. Spatial Analysis Workflow
- Ask questions
- Explore and prepare data
- Analyze and model
- Interpret results
- Repeat or modify
- Present results
- Make decisions